Gemological Grading Systems – Diamond Grading
There are no laws that regulate how diamonds are graded. There are differences among different grading companies and organizations. We strive to offer diamond grading reports that have a simple, straightforward, and intuitive scale to provide all the information you need to be comfortable in your diamond-buying decision. GGS maintains an excellent reputation with consumers and the trade for accurate, consistent diamond grading.
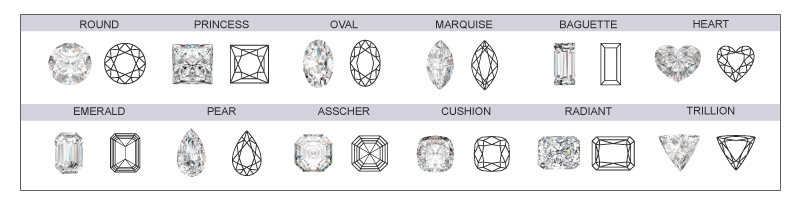
Diamond Shape and Cut
Each diamond is described as to its shape (round, oval, pear, etc.) and its cut (brilliant, etc.)
Diamond Karat Size or Weight
The karat is the unit of measurement for the physical weight of diamonds. One karat equals 0.200 grams or 1/5 gram, and is subdivided into 100 points. For comparison, in units more familiar in the United States, one karat equals 0.007 ounce avoirdupois.
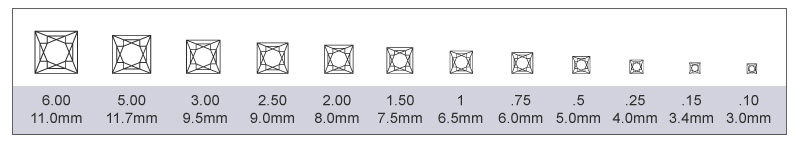
Karat Weight is the most objective of the diamond’s 4Cs. It involves no estimates, comparisons, or judgments. Large diamonds are rarer than smaller ones, and as the karat weight increases, the value of the diamond increases as well. However, the increase in value is not proportionate to the size increase. For example, a one-karat diamond will cost more than twice that of a ½-karat diamond (assuming Color, Clarity, and Cut grade are the same). Weight does not always enhance the value of a diamond, either. Two diamonds of equal weight may be unequal in value, depending upon other determining factors such as Cut, Color, and Clarity. In fact, if a diamond is improperly cut, the added weight may serve only to reduce its brilliance.
GGS Clarity Grading Scale
Diamond size has an effect on clarity. It is easier to see an inclusion in a larger diamond than in a small one. Diamonds with clarity grades of I1 I2 I3 will have eye-visible inclusions. Some SI1 SI2 SI3 stones can have eye-visible inclusions, depending on your visual acuity and how hard you look.
These verbal descriptors are trade terms originally developed to describe diamonds for diamond manufacturers and retailers. Over time, these terms have become recognized at the consumer level and, because they are now widely accepted, GGS adheres to them as well. The Grades are from highest to lowest in Clarity quality as follows:
- Flawless/Internally Flawless (F/IF) Very rare for diamonds!
- Very, Very Slightly Included (VVS1 and VVS2) Also very rare.
- Very Slightly Included (VS1 and VS2)
- Slightly Included (SI1 SI2, SI3)
- Included (I1, I2, and I3)
|
FL – IF |
VVS1 – VVS2 |
VS1 – VS2 |
SI1 – SI2 SI3 |
I1 – I2 – I3 |
|
INTERNALLY FLAWLESS |
VERY,VERY SLIGHTLY INCLUDED |
VERY SLIGHTLY INCLUDED |
SLIGHTLY INCLUDED |
INCLUDED |
GGS Color Grading Scale
Color actually refers to the absence of color in a diamond. The less yellow within the diamond, the higher on the alphabetical scale the diamond will be graded. Colorless diamonds are D-F, near colorless are G-J, faint yellow are K-M, very light yellow are N-R. S-Z are light yellow. Colorless diamonds are higher priced in the colorless to yellow or colorless to brown diamond ranges. However, many people like the warmth of a faint to light yellow or brown diamond. If that describes you, then you can find great value in that particular type of diamond.
|
D E F |
G H I J |
K L M |
N O P Q R |
S T U V W X Y Z |
|
COLORLESS |
NEAR COLORLESS |
FAINT YELLOW |
VERY LIGHT YELLOW |
LIGHT YELLOW |
Proportions
The items in this category relate to the cut (or make) of the diamond:
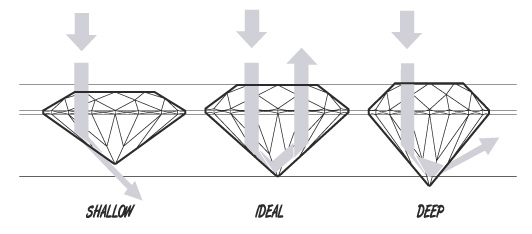
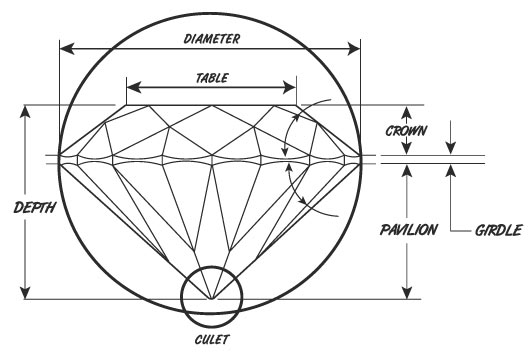
- Depth Percentage: The relationship between the depth and the average diameter of a diamond.
- Table: The relationship between the table (flat, top facet) and the average diameter.
- Girdle: Describes the variance and relative width at minimum and maximum positions. The girdle is the rim that separates the top and the bottom of the diamond.
- Culet: The bottom facet of a diamond as viewed through the table.
- Polish: Refers to the quality of the surface of a diamond.
- Symmetry: General comment regarding the symmetry of the diamond.
 Â
Â
Fluorescence
Fluorescence describes the degree of sensitivity of a diamond to long wave ultraviolet radiation. None or blue is fine. GGS recommends that you avoid orange, yellow, and green.

